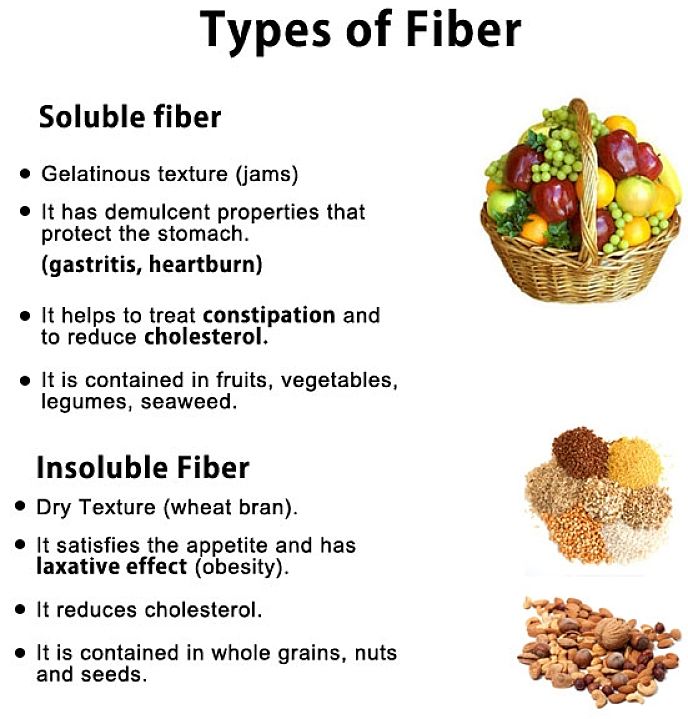
Dietary Fiber Chart - Best Foods Rich in Natural Fiber
Fibre (Dietary Fiber) has a lot of health benefits including helping digestion, keeping the body regular, lowering cholesterol, reducing the risk of bowel cancer and helping with weight loss programs. While fibre is essentially indigestible and contains no nutrients, it is the physical features of fiber that are important. All plant based whole foods, such as fruits and vegetables contain some fibre and certain vegetables, grains and beans are particularly rich in natural fibre.
The problem with modern diets is that when food is processed the fibre is removed. The classic examples of this are the processing of wholemeal flour into white flour and brown flour into white rice. Many of the nutrients in whole wheat flour and brown rice are removed when it is processed to remove the fibre. In this article I will outline the foods to eat to ensure you have adequate fibre in your diet, and the many health benefits of fibre.
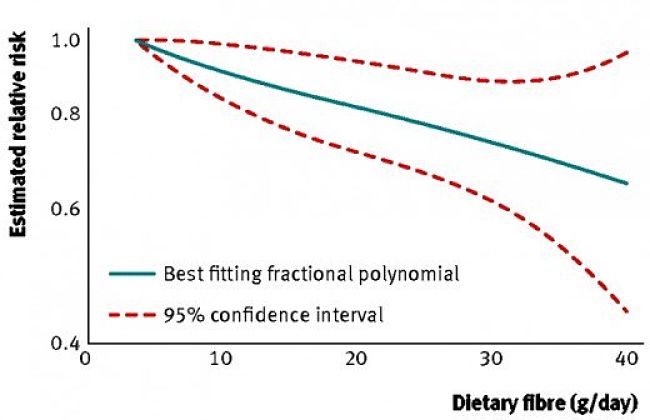
Fibre and Colon Cancer
Despite the claims that fiber in the diet helps to reduce the risk of colon cancer the research has been contradictory.Two studies reported in the The Lancet (Lancet. 2003;361:1491-1495, 1496-1501) showed that in populations with low average intake of dietary fiber,
an approximate doubling of total fiber intake from foods could reduce the risk of colorectal cancer by 40%.
A very large study of study of 89,000 US nurses (New England Journal of Medicine 1999; 340:169-76) found no correlation
between dietary fiber and colon cancer.
Researchers in London conducted a large and comprehensive review of previous studies that suggested a possible explanation.
Their review of 25 previous research studies illustrated that the natural fibre in vegetable and fruit was not very effective.
However they showed an association between fibre in whole grains and cereals and reduced risk of colorectal cancer.
They concluded that every additional 10g of fibre a day that is added to the diet, reduced the risk of bowel cancer by about 10 percent.
Whole grain foods rich in fibre include unprocessed cereals and grains, brown rice, whole grain breads, porridge and oatmeal. Many commercial packaged breakfast cereals that are available in various countries are rich in fibre levels (such as All-Bran).
Fibre and Weight Loss
The benefits of fibre in weight loss programs is largely misunderstood and linked to various myths about negative calorie foods (see: Facts about Negative Calorie Foods - Calorie Density is What Matters).The concept is that certain high fibre foods such as celery contain so few calories and require so much energy to break down in the stomach and intestine that they represent a net calorie loss to your body. While this is untrue except in ridiculous examples such as eating paper, high fibre foods are still a very important part of a weight loss program. The issues are portion size, calorie density, bulk in foods and processing and digestion times in the stomach and small intestine.
Whole foods such as whole grains, beans and cereals have reduce calorie densities compared with there processed equivalents. Foods such as celery, cabbage, lettuce and many salad greens contain high fibre and high levels of cellulose that the body cannot digest. These foods provide bulk and increase the feeling of fullness while yielding very few calories. Replacing high calorie and processed foods with these food with low calorie density helps reduce calorie intake while giving people a sense of fullness which reduces the amount that people eat. Calorie density simply means the number of calories in a cup or other measure of the volume of food. ref here
General Health Benefits of Fibre
Some of the general health benefits of fiber include:
- constipation,
- hemorrhoids,
- diverticulosis,
- high blood sugar,
- high cholesterol,
- high blood pressure,
- obesity,
- diabetes, and
- heart disease
List of Foods with their Fibre Contents
|
Food
|
Serving Size
|
Fiber (g)
|
|---|---|---|
|
Bran cereal
|
1 cup
|
19.9
|
|
Black beans, cooked
|
1 cup
|
13.9
|
|
Lentils, red cooked
|
1 cup
|
13.6
|
|
Oats, rolled dry
|
1 cup
|
12
|
|
Avocado (fruit)
|
1 medium
|
11.8
|
|
Kidney beans, cooked
|
1 cup
|
11.6
|
|
Peas, cooked
|
1 cup
|
8.8
|
|
Lima beans, cooked
|
1 cup
|
8.6
|
|
Soybeans, cooked
|
1 cup
|
8.6
|
|
Quinoa, cooked
|
1 cup
|
8.4
|
|
Brown rice, dry
|
1 cup
|
7.9
|
|
Kale, cooked
|
1 cup
|
7.2
|
|
Flax seeds
|
3 Tbsp.
|
6.9
|
|
Raspberries
|
1 cup
|
6.4
|
|
Pasta, whole wheat
|
1 cup
|
6.3
|
|
Quinoa (seeds) dry
|
1/4 cup
|
6.2
|
|
Winter squash, cooked
|
1 cup
|
6.2
|
|
Garbanzo beans, cooked
|
1 cup
|
5.8
|
|
Carrot, cooked
|
1 cup
|
5.2
|
|
Pear
|
1 medium
|
5.1
|
|
Apples with skin
|
1 medium
|
5
|
|
Sweet potato, cooked
|
1 medium
|
4.9
|
|
Potato, baked w/ skin
|
1 medium
|
4.8
|
|
Corn, sweet
|
1 cup
|
4.6
|
|
Broccoli, cooked
|
1 cup
|
4.5
|
|
Strawberries
|
1 cup
|
4.4
|
|
Spinach, cooked
|
1 cup
|
4.3
|
|
Blueberries
|
1 cup
|
4.2
|
|
Almonds
|
1 oz
|
4.2
|
|
Beet greens
|
1 cup
|
4.2
|
|
Cabbage, cooked
|
1 cup
|
4.2
|
|
Pumpkin seeds
|
1/4 cup
|
4.1
|
|
Cole slaw
|
1 cup
|
4
|
|
Green beans
|
1 cup
|
4
|
|
Banana
|
1 medium
|
3.9
|
|
Figs, dried
|
2 medium
|
3.7
|
|
Swiss chard, cooked
|
1 cup
|
3.7
|
|
Brussels sprouts, cooked
|
1 cup
|
3.6
|
|
Air-popped Popcorn
|
3 cups
|
3.6
|
|
Orange, navel
|
1 medium
|
3.4
|
|
Cauliflower, cooked
|
1 cup
|
3.4
|
|
Peaches, dried
|
3 pieces
|
3.2
|
|
Grapefruit
|
1/2 medium
|
3.1
|
|
Pistachio nuts
|
1 oz
|
3.1
|
|
Walnuts
|
1 oz
|
3.1
|
|
Sunflower seeds
|
1/4 cup
|
3
|
|
Apricots, dried
|
4 pieces
|
2.9
|
|
Onions, raw
|
1 cup
|
2.9
|
|
Beets, cooked
|
1 cup
|
2.8
|
|
Bok choy, cooked
|
1 cup
|
2.8
|
|
Carrot
|
1 medium
|
2.6
|
|
Collard greens, cooked
|
1 cup
|
2.6
|
|
Peppers, sweet
|
1 cup
|
2.6
|
|
Zucchini, cooked
|
1 cup
|
2.6
|
|
Summer squash, cooked
|
1 cup
|
2.5
|
|
Peanuts
|
1 oz
|
2.3
|
|
Peach
|
1 medium
|
2
|
|
Bread, whole wheat
|
1 slice
|
2
|
|
Raisins
|
1.5 oz box
|
1.6
|
|
Cantaloupe, cubes
|
1 cup
|
1.3
|
|
Plum
|
1 medium
|
1.1
|
|
Celery
|
1 stalk
|
1.1
|
|
Apricot
|
3 medium
|
1
|
|
Cashews
|
1 oz
|
1
|
|
Tomato
|
1 medium
|
1
|
Related Articles about Fiber in Foods
=> Why Calorie Counts for Protein and Fiber are Inaccurate
=> High Protein, High Fiber Food Lists and Diet Plan
=> Best Fruit for Weight Loss with Calorie, Fiber and Nutrition
=> Best Healthy Vegetable Chart - Calories, Fiber, Vitamins, Minerals
=> High Fiber Diet May Help Asthma Sufferers Via Fermentable Carbohydrates
=> Bowel Cancer Risk Reduced by Eating Whole Grains, Bran, Fiber Rich Foods